请注意,本文编写于 185 天前,最后修改于 185 天前,其中某些信息可能已经过时。
目录
引言
在现代软件开发中,我们经常需要处理复杂的数据查询场景。特别是在处理大量搜索条件时,传统的静态LINQ查询可能会变得冗长且难以维护。Predicate Builder作为一个强大的工具,为我们提供了一种优雅的方式来构建动态LINQ查询。本文将深入探讨Predicate Builder的使用方法,并提供多个实际应用示例。
Predicate Builder概述
Predicate Builder最初由Joe Albahari提出,后来由Pete Montgomery扩展为Universal PredicateBuilder。它允许开发者像编写动态SQL一样构建LINQ查询,特别适用于需要处理多个搜索条件的场景。
为什么选择Predicate Builder?
- 代码简洁性: 减少冗长的if/else语句
- 性能优化: 动态构建查询通常比静态查询更高效
- 灵活性: 可根据运行时条件动态调整查询逻辑
- 可读性: 使复杂查询逻辑更易理解和维护
Predicate Builder的基本实现
首先,让我们看一下Predicate Builder的核心实现:
C#public static class PredicateBuilder
{
public static Expression<Func<T, bool>> True<T>() => f => true;
public static Expression<Func<T, bool>> False<T>() => f => false;
public static Expression<Func<T, bool>> Or<T>(this Expression<Func<T, bool>> expr1,
Expression<Func<T, bool>> expr2)
{
var invokedExpr = Expression.Invoke(expr2, expr1.Parameters.Cast<Expression>());
return Expression.Lambda<Func<T, bool>>
(Expression.OrElse(expr1.Body, invokedExpr), expr1.Parameters);
}
public static Expression<Func<T, bool>> And<T>(this Expression<Func<T, bool>> expr1,
Expression<Func<T, bool>> expr2)
{
var invokedExpr = Expression.Invoke(expr2, expr1.Parameters.Cast<Expression>());
return Expression.Lambda<Func<T, bool>>
(Expression.AndAlso(expr1.Body, invokedExpr), expr1.Parameters);
}
}
实际应用示例
让我们通过一些实际的例子来展示Predicate Builder的强大功能。
示例1: 图书馆查询系统
假设我们有一个Book类:
C#using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Linq.Expressions;
public class Book
{
public int Id { get; set; }
public string Title { get; set; }
public string Author { get; set; }
public int PublicationYear { get; set; }
public string Genre { get; set; }
public bool IsAvailable { get; set; }
}
public class Library
{
private List<Book> books = new List<Book>();
public Library()
{
// 添加一些示例书籍
books.Add(new Book { Id = 1, Title = "1984", Author = "George Orwell", PublicationYear = 1949, Genre = "Science Fiction", IsAvailable = true });
books.Add(new Book { Id = 2, Title = "To Kill a Mockingbird", Author = "Harper Lee", PublicationYear = 1960, Genre = "Fiction", IsAvailable = false });
books.Add(new Book { Id = 3, Title = "The Great Gatsby", Author = "F. Scott Fitzgerald", PublicationYear = 1925, Genre = "Fiction", IsAvailable = true });
books.Add(new Book { Id = 4, Title = "Pride and Prejudice", Author = "Jane Austen", PublicationYear = 1813, Genre = "Romance", IsAvailable = true });
}
public IEnumerable<Book> SearchBooks(string titleKeyword, string author, int? fromYear, int? toYear, string genre, bool? isAvailable)
{
var predicate = PredicateBuilder.True<Book>();
if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(titleKeyword))
predicate = predicate.And(b => b.Title.Contains(titleKeyword));
if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(author))
predicate = predicate.And(b => b.Author.Contains(author));
if (fromYear.HasValue)
predicate = predicate.And(b => b.PublicationYear >= fromYear.Value);
if (toYear.HasValue)
predicate = predicate.And(b => b.PublicationYear <= toYear.Value);
if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(genre))
predicate = predicate.And(b => b.Genre == genre);
if (isAvailable.HasValue)
predicate = predicate.And(b => b.IsAvailable == isAvailable.Value);
return books.AsQueryable().Where(predicate);
}
}
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Library library = new Library();
// 示例查询
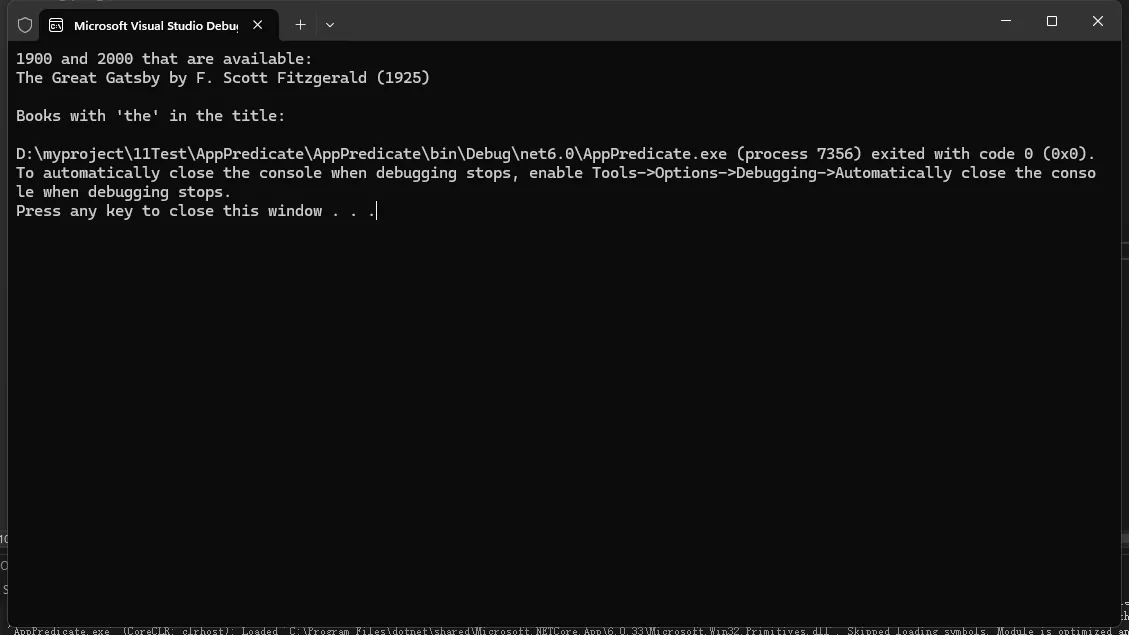
var result1 = library.SearchBooks("", "", 1900, 2000, "Fiction", true);
Console.WriteLine("1900 and 2000 that are available:");
foreach (var book in result1)
{
Console.WriteLine($"{book.Title} by {book.Author} ({book.PublicationYear})");
}
Console.WriteLine();
var result2 = library.SearchBooks("the", "", null, null, "", null);
Console.WriteLine("Books with 'the' in the title:");
foreach (var book in result2)
{
Console.WriteLine($"{book.Title} by {book.Author}");
}
}
}
示例2: 员工管理系统
C#using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Linq.Expressions;
public class Employee
{
public int Id { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
public string Department { get; set; }
public decimal Salary { get; set; }
public DateTime HireDate { get; set; }
public bool IsActive { get; set; }
}
public class Company
{
private List<Employee> employees = new List<Employee>();
public Company()
{
// 添加一些示例员工
employees.Add(new Employee { Id = 1, Name = "John Doe", Department = "IT", Salary = 75000, HireDate = new DateTime(2019, 1, 15), IsActive = true });
employees.Add(new Employee { Id = 2, Name = "Jane Smith", Department = "HR", Salary = 65000, HireDate = new DateTime(2020, 3, 1), IsActive = true });
employees.Add(new Employee { Id = 3, Name = "Mike Johnson", Department = "Finance", Salary = 80000, HireDate = new DateTime(2018, 6, 10), IsActive = true });
employees.Add(new Employee { Id = 4, Name = "Emily Brown", Department = "IT", Salary = 70000, HireDate = new DateTime(2021, 2, 20), IsActive = false });
}
public IEnumerable<Employee> SearchEmployees(string[] departments, decimal? minSalary, decimal? maxSalary, DateTime? hiredAfter, bool? isActive)
{
var predicate = PredicateBuilder.True<Employee>();
if (departments != null && departments.Length > 0)
{
var deptPredicate = PredicateBuilder.False<Employee>();
foreach (var dept in departments)
{
string tempDept = dept;
deptPredicate = deptPredicate.Or(e => e.Department == tempDept);
}
predicate = predicate.And(deptPredicate);
}
if (minSalary.HasValue)
predicate = predicate.And(e => e.Salary >= minSalary.Value);
if (maxSalary.HasValue)
predicate = predicate.And(e => e.Salary <= maxSalary.Value);
if (hiredAfter.HasValue)
predicate = predicate.And(e => e.HireDate >= hiredAfter.Value);
if (isActive.HasValue)
predicate = predicate.And(e => e.IsActive == isActive.Value);
return employees.AsQueryable().Where(predicate);
}
}
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Company company = new Company();
// 示例查询
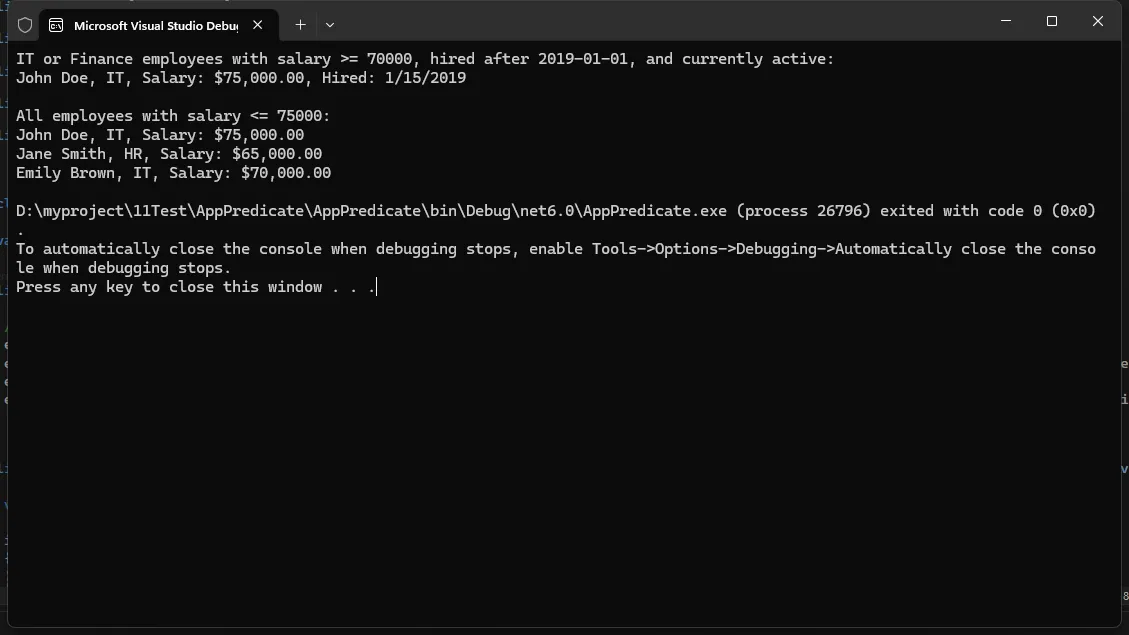
var result1 = company.SearchEmployees(new string[] { "IT", "Finance" }, 70000, null, new DateTime(2019, 1, 1), true);
Console.WriteLine("IT or Finance employees with salary >= 70000, hired after 2019-01-01, and currently active:");
foreach (var employee in result1)
{
Console.WriteLine($"{employee.Name}, {employee.Department}, Salary: {employee.Salary:C}, Hired: {employee.HireDate.ToShortDateString()}");
}
Console.WriteLine();
var result2 = company.SearchEmployees(null, null, 75000, null, null);
Console.WriteLine("All employees with salary <= 75000:");
foreach (var employee in result2)
{
Console.WriteLine($"{employee.Name}, {employee.Department}, Salary: {employee.Salary:C}");
}
}
}
性能考虑
使用Predicate Builder构建动态查询通常比编写静态查询更高效,特别是在处理大量条件组合时。它减少了不必要的数据库查询,因为所有条件都被组合成一个表达式树,然后一次性发送到数据库。
最佳实践
- 正确处理null值和空字符串
- 对于复杂查询,考虑使用数据库索引以提高性能
- 在大型项目中,创建一个通用的查询构建器类来封装常用的查询逻辑
- 使用参数化查询来防止SQL注入攻击
- 考虑使用缓存来优化频繁执行的查询
结论
Predicate Builder为C#开发者提供了一个强大的工具,用于创建灵活且高效的动态LINQ查询。通过本文的示例,我们看到了如何在各种场景下应用Predicate Builder,从简单的条件过滤到复杂的多条件组合查询。这种方法不仅提高了代码的可读性和可维护性,还能在处理复杂查询场景时提供更好的性能。
本文作者:rick
本文链接:
版权声明:本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 BY-NC-SA 许可协议。转载请注明出处!
目录