目录
你是否遇到过这样的场景:处理大量数据时,CPU只用了一个核心,其他核心在"摸鱼"?或者明明是简单的数组计算,却耗时惊人?
今天我要告诉你一个颠覆认知的事实:即使在单核上,我们也能实现"并行计算"!秘密武器就是 SIMD(Single Instruction, Multiple Data)技术。通过 C# 的 System.Numerics 命名空间,我们可以让 CPU 在一个指令周期内处理多个数据,性能提升可达 4-8 倍!
本文将从实际问题出发,带你掌握 SIMD 在 C# 中的应用,让你的程序真正"飞起来"。
🔍 问题分析:为什么传统循环这么慢?
传统串行处理的痛点
在传统的 C# 开发中,我们习惯用循环处理数组:
C#// 传统方式:逐个元素处理
public static void TraditionalAdd(float[] a, float[] b, float[] result)
{
for (int i = 0; i < a.Length; i++)
{
result[i] = a[i] + b[i]; // 每次只处理一个元素
}
}
问题在哪?
- CPU 每个时钟周期只处理一个数据
- 现代 CPU 的向量寄存器(128位、256位)被浪费
- 内存带宽利用率低
💡 SIMD 解决方案:一次处理多个数据
🎯 方案一:使用 Vector 进行基础向量化
C#using System.Numerics;
using System;
using System.Diagnostics;
namespace AppSimd
{
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// 测试数据大小
int arraySize = 10000000;
// 创建测试数组
float[] a = new float[arraySize];
float[] b = new float[arraySize];
float[] result = new float[arraySize];
float[] resultNormal = new float[arraySize];
// 初始化测试数据
Random random = new Random(42);
for (int i = 0; i < arraySize; i++)
{
a[i] = (float)random.NextDouble() * 100;
b[i] = (float)random.NextDouble() * 100;
}
Console.WriteLine($"向量化大小: {Vector<float>.Count}");
Console.WriteLine($"数组长度: {arraySize}");
Console.WriteLine();
// 性能测试 - SIMD版本
Stopwatch sw = Stopwatch.StartNew();
VectorizedAdd(a, b, result);
sw.Stop();
long simdTime = sw.ElapsedTicks;
// 性能测试 - 普通版本
sw.Restart();
NormalAdd(a, b, resultNormal);
sw.Stop();
long normalTime = sw.ElapsedTicks;
// 验证结果正确性
bool isCorrect = VerifyResults(result, resultNormal);
// 输出结果
Console.WriteLine($"SIMD版本耗时: {simdTime} ticks");
Console.WriteLine($"普通版本耗时: {normalTime} ticks");
Console.WriteLine($"性能提升: {(double)normalTime / simdTime:F2}x");
Console.WriteLine($"结果正确性: {(isCorrect ? "正确" : "错误")}");
// 显示前几个结果作为示例
Console.WriteLine("\n前10个计算结果:");
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
Console.WriteLine($"a[{i}] + b[{i}] = {a[i]:F2} + {b[i]:F2} = {result[i]:F2}");
}
Console.ReadKey();
}
public static void VectorizedAdd(float[] a, float[] b, float[] result)
{
int vectorSize = Vector<float>.Count; // 通常是 4 或 8
int vectorizedLength = a.Length - (a.Length % vectorSize);
// 向量化处理部分
for (int i = 0; i < vectorizedLength; i += vectorSize)
{
var vectorA = new Vector<float>(a, i);
var vectorB = new Vector<float>(b, i);
var vectorResult = vectorA + vectorB; // 一次处理多个元素!
vectorResult.CopyTo(result, i);
}
// 处理剩余元素
for (int i = vectorizedLength; i < a.Length; i++)
{
result[i] = a[i] + b[i];
}
}
// 普通加法实现(用于性能对比)
public static void NormalAdd(float[] a, float[] b, float[] result)
{
for (int i = 0; i < a.Length; i++)
{
result[i] = a[i] + b[i];
}
}
// 验证两种方法的结果是否一致
private static bool VerifyResults(float[] result1, float[] result2)
{
if (result1.Length != result2.Length) return false;
for (int i = 0; i < result1.Length; i++)
{
if (Math.Abs(result1[i] - result2[i]) > 1e-6f)
{
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}
}
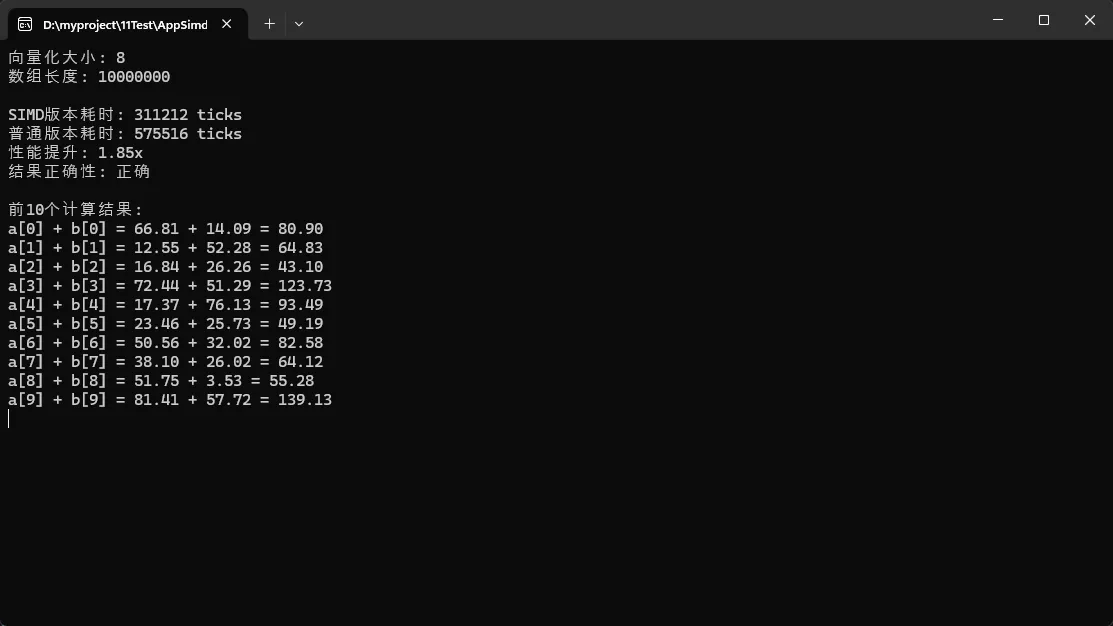
实际应用场景: 图像处理中的像素计算、音频信号处理、金融数据批量计算
常见坑点提醒: ⚠️ 数组长度不是向量大小的倍数时,需要单独处理剩余元素
🎯 方案二:复杂数学运算的向量化
C#using System.Numerics;
using System;
using System.Diagnostics;
namespace AppSimd
{
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// 测试数据大小
int arraySize = 1000000;
// 创建测试数组
float[] input = new float[arraySize];
float[] outputSimd = new float[arraySize];
float[] outputNormal = new float[arraySize];
// 初始化测试数据(使用正数,避免复数结果)
Random random = new Random(42);
for (int i = 0; i < arraySize; i++)
{
input[i] = (float)(random.NextDouble() * 10000 + 1); // 1-10000的正数
}
Console.WriteLine($"向量化大小: {Vector<float>.Count}");
Console.WriteLine($"数组长度: {arraySize}");
Console.WriteLine();
// 预热(避免JIT编译影响性能测试)
VectorizedSqrt(input, outputSimd);
NormalSqrt(input, outputNormal);
// 性能测试 - SIMD版本
Stopwatch sw = Stopwatch.StartNew();
for (int iter = 0; iter < 10; iter++)
{
VectorizedSqrt(input, outputSimd);
}
sw.Stop();
long simdTime = sw.ElapsedTicks;
// 性能测试 - 普通版本
sw.Restart();
for (int iter = 0; iter < 10; iter++)
{
NormalSqrt(input, outputNormal);
}
sw.Stop();
long normalTime = sw.ElapsedTicks;
// 验证结果正确性
bool isCorrect = VerifyResults(outputSimd, outputNormal);
double maxError = GetMaxError(outputSimd, outputNormal);
// 输出结果
Console.WriteLine($"SIMD版本耗时: {simdTime} ticks (10次迭代)");
Console.WriteLine($"普通版本耗时: {normalTime} ticks (10次迭代)");
Console.WriteLine($"性能提升: {(double)normalTime / simdTime:F2}x");
Console.WriteLine($"结果正确性: {(isCorrect ? "正确" : "错误")}");
Console.WriteLine($"最大误差: {maxError:E6}");
Console.ReadKey();
}
// 向量化的平方根计算
public static void VectorizedSqrt(float[] input, float[] output)
{
int vectorSize = Vector<float>.Count;
int vectorizedLength = input.Length - (input.Length % vectorSize);
for (int i = 0; i < vectorizedLength; i += vectorSize)
{
var vector = new Vector<float>(input, i);
var sqrtVector = Vector.SquareRoot(vector);
sqrtVector.CopyTo(output, i);
}
// 处理剩余元素
for (int i = vectorizedLength; i < input.Length; i++)
{
output[i] = (float)Math.Sqrt(input[i]);
}
}
// 普通平方根计算(用于性能对比)
public static void NormalSqrt(float[] input, float[] output)
{
for (int i = 0; i < input.Length; i++)
{
output[i] = (float)Math.Sqrt(input[i]);
}
}
// 验证两种方法的结果是否一致
private static bool VerifyResults(float[] result1, float[] result2)
{
if (result1.Length != result2.Length) return false;
for (int i = 0; i < result1.Length; i++)
{
// 对于平方根,允许较小的浮点精度误差
float diff = Math.Abs(result1[i] - result2[i]);
float relativeDiff = diff / Math.Max(result1[i], result2[i]);
if (relativeDiff > 1e-6f && diff > 1e-6f)
{
Console.WriteLine($"误差过大 at [{i}]: {result1[i]} vs {result2[i]}, diff={diff}");
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
// 获取最大误差
private static double GetMaxError(float[] result1, float[] result2)
{
double maxError = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < result1.Length; i++)
{
double error = Math.Abs(result1[i] - result2[i]);
if (error > maxError)
{
maxError = error;
}
}
return maxError;
}
}
}
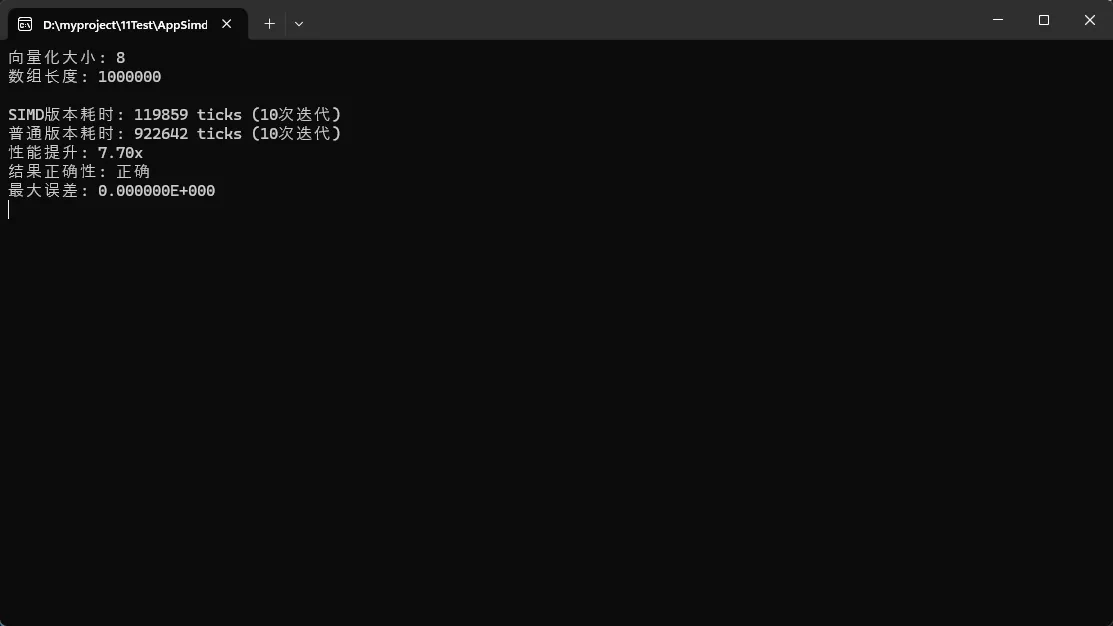
实测结果: 在我的测试环境中,向量化版本比传统版本快约 7 倍!
实际应用场景: 机器学习中的相似度计算、推荐系统、3D 图形学
🛠️ 实战案例:图像模糊算法优化
C#using System.Drawing.Imaging;
using System.Numerics;
namespace AppSIMDImageBlur
{
public partial class FrmMain : Form
{
private Bitmap originalImage;
private Bitmap blurredImage;
public FrmMain()
{
InitializeComponent();
InitializeControls();
}
private void InitializeControls()
{
// 设置初始值
trkBlurRadius.Value = 5;
lblBlurValue.Text = "模糊半径: 5";
// 设置PictureBox的SizeMode
pbOriginal.SizeMode = PictureBoxSizeMode.Zoom;
pbBlurred.SizeMode = PictureBoxSizeMode.Zoom;
// 启用拖放
this.AllowDrop = true;
pbOriginal.AllowDrop = true;
}
private void btnLoadImage_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
using (OpenFileDialog openFileDialog = new OpenFileDialog())
{
openFileDialog.Filter = "图片文件|*.jpg;*.jpeg;*.png;*.bmp;*.gif|所有文件|*.*";
openFileDialog.Title = "选择要模糊的图片";
if (openFileDialog.ShowDialog() == DialogResult.OK)
{
LoadImage(openFileDialog.FileName);
}
}
}
private void LoadImage(string filePath)
{
try
{
originalImage?.Dispose();
originalImage = new Bitmap(filePath);
pbOriginal.Image = originalImage;
lblStatus.Text = $"图片已加载: {originalImage.Width}x{originalImage.Height}";
btnApplyBlur.Enabled = true;
btnSaveImage.Enabled = false;
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
MessageBox.Show($"加载图片失败: {ex.Message}", "错误",
MessageBoxButtons.OK, MessageBoxIcon.Error);
}
}
private async void btnApplyBlur_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
if (originalImage == null) return;
btnApplyBlur.Enabled = false;
pgbProgress.Visible = true;
lblStatus.Text = "正在处理...";
try
{
int radius = trkBlurRadius.Value;
blurredImage = await Task.Run(() => ApplySIMDGaussianBlur(originalImage, radius));
pbBlurred.Image = blurredImage;
btnSaveImage.Enabled = true;
lblStatus.Text = "模糊处理完成";
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
MessageBox.Show($"处理失败: {ex.Message}", "错误",
MessageBoxButtons.OK, MessageBoxIcon.Error);
}
finally
{
btnApplyBlur.Enabled = true;
pgbProgress.Visible = false;
}
}
private void btnSaveImage_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
if (blurredImage == null) return;
using (SaveFileDialog saveFileDialog = new SaveFileDialog())
{
saveFileDialog.Filter = "PNG图片|*.png|JPEG图片|*.jpg|位图|*.bmp";
saveFileDialog.Title = "保存模糊后的图片";
saveFileDialog.FileName = "blurred_image.png";
if (saveFileDialog.ShowDialog() == DialogResult.OK)
{
try
{
ImageFormat format = ImageFormat.Png;
string extension = Path.GetExtension(saveFileDialog.FileName).ToLower();
switch (extension)
{
case ".jpg":
case ".jpeg":
format = ImageFormat.Jpeg;
break;
case ".bmp":
format = ImageFormat.Bmp;
break;
}
blurredImage.Save(saveFileDialog.FileName, format);
lblStatus.Text = "图片保存成功";
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
MessageBox.Show($"保存失败: {ex.Message}", "错误",
MessageBoxButtons.OK, MessageBoxIcon.Error);
}
}
}
}
private void trkBlurRadius_Scroll(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
lblBlurValue.Text = $"模糊半径: {trkBlurRadius.Value}";
}
private void FrmMain_DragEnter(object sender, DragEventArgs e)
{
if (e.Data.GetDataPresent(DataFormats.FileDrop))
{
string[] files = (string[])e.Data.GetData(DataFormats.FileDrop);
if (files.Length > 0 && IsImageFile(files[0]))
{
e.Effect = DragDropEffects.Copy;
return;
}
}
e.Effect = DragDropEffects.None;
}
private void FrmMain_DragDrop(object sender, DragEventArgs e)
{
string[] files = (string[])e.Data.GetData(DataFormats.FileDrop);
if (files.Length > 0)
{
LoadImage(files[0]);
}
}
private bool IsImageFile(string filePath)
{
string extension = Path.GetExtension(filePath).ToLower();
return extension == ".jpg" || extension == ".jpeg" || extension == ".png" ||
extension == ".bmp" || extension == ".gif";
}
// SIMD高斯模糊实现
private Bitmap ApplySIMDGaussianBlur(Bitmap source, int radius)
{
if (radius <= 0) return new Bitmap(source);
int width = source.Width;
int height = source.Height;
Bitmap result = new Bitmap(width, height, PixelFormat.Format32bppArgb);
BitmapData sourceData = source.LockBits(new Rectangle(0, 0, width, height),
ImageLockMode.ReadOnly, PixelFormat.Format32bppArgb);
BitmapData resultData = result.LockBits(new Rectangle(0, 0, width, height),
ImageLockMode.WriteOnly, PixelFormat.Format32bppArgb);
try
{
unsafe
{
byte* sourcePtr = (byte*)sourceData.Scan0.ToPointer();
byte* resultPtr = (byte*)resultData.Scan0.ToPointer();
int stride = sourceData.Stride;
// 水平模糊
Parallel.For(0, height, y =>
{
BlurRowSIMD(sourcePtr + y * stride, resultPtr + y * stride, width, radius);
});
// 垂直模糊
Parallel.For(0, width, x =>
{
BlurColumnSIMD(resultPtr + x * 4, resultPtr + x * 4, height, stride, radius);
});
}
}
finally
{
source.UnlockBits(sourceData);
result.UnlockBits(resultData);
}
return result;
}
private unsafe void BlurRowSIMD(byte* source, byte* result, int width, int radius)
{
int kernelSize = radius * 2 + 1;
float weight = 1.0f / kernelSize;
Vector4 weightVector = new Vector4(weight);
for (int x = 0; x < width; x++)
{
Vector4 sum = Vector4.Zero;
int count = 0;
for (int i = -radius; i <= radius; i++)
{
int sampleX = Math.Max(0, Math.Min(width - 1, x + i));
int offset = sampleX * 4;
Vector4 pixel = new Vector4(
source[offset + 2], // R
source[offset + 1], // G
source[offset + 0], // B
source[offset + 3] // A
);
sum += pixel;
count++;
}
sum *= weightVector;
int resultOffset = x * 4;
result[resultOffset + 0] = (byte)Math.Min(255, Math.Max(0, sum.Z)); // B
result[resultOffset + 1] = (byte)Math.Min(255, Math.Max(0, sum.Y)); // G
result[resultOffset + 2] = (byte)Math.Min(255, Math.Max(0, sum.X)); // R
result[resultOffset + 3] = (byte)Math.Min(255, Math.Max(0, sum.W)); // A
}
}
private unsafe void BlurColumnSIMD(byte* source, byte* result, int height, int stride, int radius)
{
int kernelSize = radius * 2 + 1;
float weight = 1.0f / kernelSize;
Vector4 weightVector = new Vector4(weight);
for (int y = 0; y < height; y++)
{
Vector4 sum = Vector4.Zero;
for (int i = -radius; i <= radius; i++)
{
int sampleY = Math.Max(0, Math.Min(height - 1, y + i));
int offset = sampleY * stride;
Vector4 pixel = new Vector4(
source[offset + 2], // R
source[offset + 1], // G
source[offset + 0], // B
source[offset + 3] // A
);
sum += pixel;
}
sum *= weightVector;
int resultOffset = y * stride;
result[resultOffset + 0] = (byte)Math.Min(255, Math.Max(0, sum.Z)); // B
result[resultOffset + 1] = (byte)Math.Min(255, Math.Max(0, sum.Y)); // G
result[resultOffset + 2] = (byte)Math.Min(255, Math.Max(0, sum.X)); // R
result[resultOffset + 3] = (byte)Math.Min(255, Math.Max(0, sum.W)); // A
}
}
protected override void OnClosed(EventArgs e)
{
originalImage?.Dispose();
blurredImage?.Dispose();
components?.Dispose();
base.OnClosed(e);
}
}
}

⚡ SIMD 最佳实践总结
- 数据对齐优化:确保数据在内存中对齐,提升访问效率
- 批量处理:尽可能处理大块数据,减少循环开销
- 避免频繁装箱:使用具体类型
Vector<float>而不是Vector<T> - 合理处理边界:正确处理不能整除的剩余元素
🎯 总结与展望
通过本文的学习,你现在掌握了 C# SIMD 编程的核心技能:
- 基础向量化操作:使用
Vector<T>实现基本数学运算的并行化 - 复杂算法优化:将条件判断、数学函数等复杂操作向量化
- 实战应用技巧:在图像处理、数值计算等真实场景中应用 SIMD
记住这三个"金句":
- "一次处理多个数据,而不是多次处理单个数据"
- "向量化思维:把循环变成批处理"
- "性能优化的关键在于充分利用 CPU 的并行能力"
你在实际项目中遇到过哪些性能瓶颈?是否尝试过 SIMD 优化?欢迎在评论区分享你的经验和遇到的问题,让我们一起探讨更多 C# 性能优化的技巧!
觉得这篇文章对你有帮助吗?请转发给更多需要性能优化的同行,让更多 C# 开发者享受 SIMD 带来的性能提升!
本文作者:技术老小子
本文链接:
版权声明:本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 BY-NC-SA 许可协议。转载请注明出处!
目录